Checksums (also known as hashes or signatures) are strings of characters made from numbers and letters, which can be used to verify the integrity of files (as well as text messages). Each file has a unique checksum, and there are many types of hashes available, such as MD5, SHA256 or CRC32.
For instance, many file hosting websites that permit downloads display checksums. After downloading a file, you can calculate its hash and compare it to the one on the website. If they don't match, it means that the file is incomplete, corrupt, modified or has other kinds of errors. Because these alphanumerical values are unique, they change at the slightest modification of the file structure according to a predefined security algorithm, depending on which cryptographic hash function is used.
We're breaking down three apps dedicated to calculating and comparing checksums, from common ones (like MD5 or SHA256) to less known ones (like BTIH or ED2K): MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility, HashTools, and HashTab. One can be accessed from a typical interface (double-click the launcher to load the main window), one gets integrated into the Windows Explorer context menu (right-click a file in Explorer and pick the app's entry), and one creates a new tab in the Properties dialog of a file (right-click a files to access the properties dialog, and go to the app's tab).
MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility
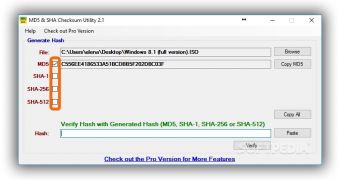
The free edition of MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility can calculate MD5, SHA1, SHA256, and SHA512 hashes as well as compare them to a pasted hash to find out if they match or not. It's fast for large files but doesn't work for multiple files at the same time and doesn't have an option for integrating the program into the Windows Explorer context menu. These features are available in the pro version (MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility Pro), along with support for CRC32 and SHA384.
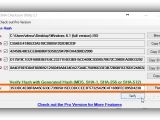
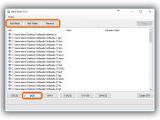
After launching the app, you can either drag and drop a file over its window or (if this doesn't work) click the Browse button near the File box and use the integrated file browser to locate and open the file.
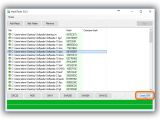
Calculations are performed automatically afterward, and all hash types are taken into account. If you're interested only in one checksum and want to speed up the computation (for large files), clear the boxes next to the hashes you don't need before adding the file. The excluded hashes can be checked for calculating them even after the file is added.
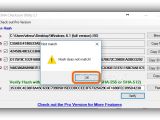
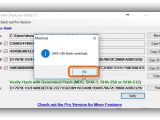
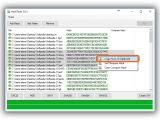
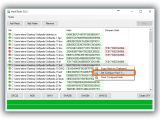
Any of the signatures can be copied by clicking on the button next to them (such as Copy MD5, doesn't copy the hash type), or you can Copy All (including the hash types). To verify file integrity, paste another checksum in the empty file next to Hash on the bottom side of the window (click Paste or press Ctrl+V), and click Verify.
For example, if you have two files and want to compare their checksums, drop the first one in the window, copy its hash (any), drop the second file to find out its signatures too, then paste the first file's hash. It will be matched against all hashes of the second file, and MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility pops up a message to tell you if the hashes are the same or not. If they are, it also tells you what type it is.
HashTools
During installation, you can allow HashTools to get integrated into the right-click menu of Explorer. However, it can also be launched from an .exe file after setup. There's also a portable version available (Portable HashTools). It supports CRC32, MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA384, and SHA512. Plus, the app can process multiple files at once as well as compare hashes.
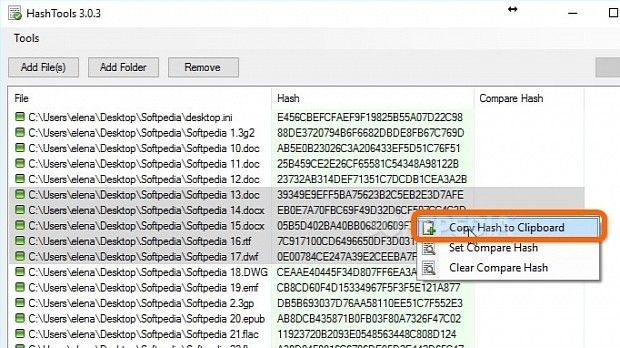
Right-click one or more selected files or folders and select Hash with HashTools. This opens the main app window, where all files are listed with their full paths. Checksums are not auto-calculated, so you can add more files to the list (click on Add File(s) or Add Folder) or Remove any of them.
It's not possible to calculate all types of signatures at once. Instead, click the button of the hash that interests you. For example, if you click MD5, HashTools calculates the MD5 checksum of all files in the list. This speeds up the calculation process if you need only a particular hash. To find out a different checksum, just click on its button (without having to reload the file list).
To copy the alphanumerical values, right-click an entry or hold down Ctrl to select multiple entries and open the right-click menu to Copy Hash to Clipboard. However, the checksum type is not copied or displayed in the list, so you have to remember which button you pressed.
To compare the hashes of two files, copy the signature of the first, right-click the second file in the list, select Set Compare Hash, paste the first file's checksum in the box, and click Ok. Unfortunately, a checksum cannot be matched against multiple selected files in the list (you can paste it for only one file at a time).
On top of that, unlike MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility, HashTools doesn't take into account all types of hashes when comparing them, so you have to try different combinations if you don't know what type it is. If the checksums match, the one in the Compare Hash column is highlighted in green (otherwise, red).
If you want to save the CRC32 hashes of all files in the list, click Create SFV to create an SFV file (they are automatically calculated), which can be later loaded in HashTools or a text editor.
HashTab
HashTab is a Windows extension that gets integrated into the Properties dialog of files, creating a new tab called File Hashes (after Compatibility and before Security). After installation, right-click a file in Explorer, click Properties, and go to the File Hashes tab. It cannot process multiple files at the same time (the new tab is not shown in the Properties dialog of folders or multiple selected files).
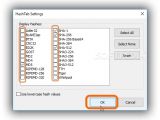
By default, the app calculates only CRC32, MD5, and SHA1. However, compared to the previous two programs, this one is far more generous concerning the supported file types: Adler32, BLAKE2sp, BTIH, CRC32, ED2K, GOST, MD2, MD4, MD5, RIPEMD128, RIPEMD256, RIPEMD320, SHA1, SHA256, SHA256 Base64, SHA384, SHA512, SHA3-224, SHA3-256, SHA3-384, SHA3-512, TTH, Tiger, and Whirlpool.
Click Settings below the Name and Hash Value list, tick the boxes of the hashes you want to calculate and clear the ones that don't interest you, in order to speed up calculations for large files. Computations are performed right away.
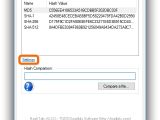
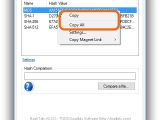
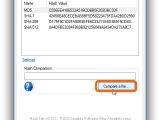
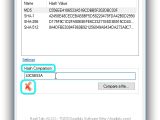
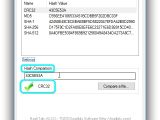
Right-click an entry to Copy the hash to the Clipboard (without the type) or to Copy All (with the type). To compare the checksums of two files, you can either paste the second file's hash in the empty box of Hash Comparison, or click Compare a file... and use the built-in file browser to locate and open the second file (its hash is auto-calculated by the tool).
The verification process is done right away, and the second hash is compared to all checksums in the list (not the ones excluded from Settings). If they match, HashTab displays a green tick icon below the Hash Comparison box and tells you the types of checksum. Otherwise, it shows a red X icon.
Check out the video guide below to see how fast these three apps can calculate the MD5 checksum of a 1GB file. You can also download MD5 & SHA Checksum Utility, HashTools, and HashTab.
How to Verify File Integrity with Checksums (MD5, SHA, CRC32)
Play our video to see how fast three Windows tools calculate the checksum of a 1GB file. Read our article to find out more about hash tools: http://www.softpedia.com/blog/how-to-verify-file-integrity-with-checksums-md5-sha-crc32-504507.shtml
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //