Quite often, network administrators use various tools to scan, test and monitor their network just to make sure everything is in place and to prevent eventual problems. Network tools come in many shapes and sizes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages so picking a tool is totally up to you, your needs and preferences. One of them is AutoScan, a network tool for exploration, monitoring and network management. This is a free software, released under the GPLv2 license and it's available for Linux graphical environments, as it's a GTK2.0-type application.
AutoScan is based on two programs: - AutoScan_Network which is somehow the visible part; - AutoScan_Agent, which is the system main part, it carries out the exploration and monitoring of the network.
To install AutoScan, you can either use the auto-installer package or the source package which needs to be compiled locally. There is also a Live CD available which provides AutoScan among other network related tools. If you choose to install AutoScan using the source package, your system needs to have a few dependencies: glib-devel, net-snmp-devel, libao-devel, libvte-devel and a few others. Fortunately, while running configure, the script will notify you which package you'll need to install.
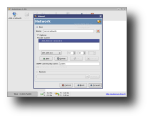
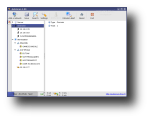
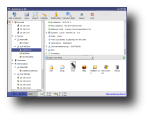
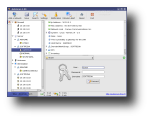
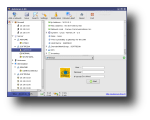
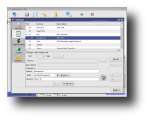
After installation, you can run AutoScan either from the shortcut under Internet in main KDE menu, or by running 'AutoScan_Network' in a terminal. On each start-up, AutoScan will run a wizard which enables you to set your network's parameters, such as the name of your network, its private subnet and the interface to be used for scanning. After those parameters are set, AutoScan starts scanning the network for each known equipment which is classified according to its type (workstation, server, router etc). When it finds an unknown equipment, it allows you to manually integrate it into the database of OS fingerprints. Moreover, according to their identification, to each equipment an icon is assigned to facilitate the visualization. These icons are customizable and can be replaced with others, as long as you copy them to /usr/share/pixmaps/AutoScan/Equipment and keep their names. Progressively with the discovery, each equipment is added in the left section of the main window, while clicking on one of them will post additional information in the right section. In particular, you can view the equipment's IP address, MAC address, open ports and several information fields which you can fill by hand (email address, name of the holder, system info etc).
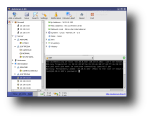
When selecting an equipment, the right section of the window also provides a list of open ports. For each port, you can associate one or more programs to be used accordingly. For instance, you can set Konqueror to start browsing that IP if a Samba share was discovered. However, for the most used ports, there is already an action set in the Open TCP Ports menu. For SSH, FTP, Telnet and other ports discovered, AutoScan allows you to use that service right from the program. AutoScan also provides an integrated Nessus client which allows connecting to a Nessus server and carrying out vulnerability tests upon the equipment. Other functions include integrated SNMP client which is able to gather additional information from the equipment which has the SNMP port activated, the ability to send messages to the equipment through the service transport (netsend), execution of pre-configured scripts (such as nmap and ping), but also others which can be manually added.
The bottom bar provides real-time information regarding the volume of data in emission and reception. It also displays the total number of found equipments, the number of equipments in course of scan/on standby of scan and the percentage of scan process.
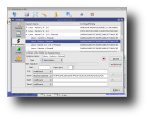
AutoScan can be configured through the Settings dialog, which is divided into five tabs. The general tab allows you to set various configuration options, such as if the program will minimize to tray, start minimize, the program's SMTP address, which audio device to use and whether the computer running it is directly connected to the Internet or through a proxy server. The Ports tab allows adding/editing/deleting ports. For each port, you can set a program to run with custom parameters. The Fingerprinting tab enables you to change/add/delete OS fingerprinting, a process of determining the operating system running on the remote host. The Scripts tab allows adding, removing or modifying commands and scripts to be run on the selected machine, while the Restore tab allows restoring a previous saved network state each time AutoStart is started.
AutoScan also provides functions used to monitor the network: notification and intrusion alert. The first will notify you when an equipment is not responding or a server is not available anymore, while the second will save the current network configuration and will notify you when new equipments are discovered on the network (useful for detecting pirate devices).
The Good
AutoScan is an easy to use tool for exploring, monitoring and managing a network. You can use it to detect equipments on the network and fetch various information about them. It's also possible to manage them through ssh and telnet, clients which are integrated into the program. One can also monitor the equipments, run custom scripts and more, right from the program's interface.
The Bad
Unfortunately, there's no documentation except for one written in French.
The Truth
If you need a simple tool for fetching various information about your network or you need to perform basic management actions on it, you may give AutoScan a try and might even be impressed with it. However, for advanced management options, you should use a more advanced tool.
Check out some screenshots below:
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //